Label Terminology
We are always here to help if you have label questions! This set of commonly-used label terms may help you to better understand the label-creation process.
PRINTING
Digital Inkjet Printing: Print process where the ink is transferred to the material with jets to recreate a digital image.
Flexographic Printing: Print process where ink is transferred to the material with separate flexible plates. Each ink color is applied in a sequence with a separate plate. The colors combine to create an image.
Screen Printing: Print process where the ink is transferred to the material through openings in a screen.
COLOR
4-Color Process: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black are printed in tiny dots. When combined, the dots blend and overlap to create a full color image.
CMYK: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black color format. Print files should be set with the CMYK color mode. This color mode is intended for printing.
RGB: Red, Green, and Blue color mode. This color mode is intended for viewing on screen and many colors can not be replicated exactly with CMYK printing.
Expanded gamut: CMYK ink plus additional ink colors. Expanded gamut helps achieve a wider range of colors than can be created with CMYK alone. Orange, Violet and Green are often the colors added in this process. Our Domino digital presses print with CMYK, Orange, Violet and White.
SPOT color: A specific non-CMYK color, often a Pantone color.
PANTONE color: Color from the PMS Pantone matching system. The Pantone Formula guide contains standardized colors that can be matched on press to the Pantone book or Pantone chips. Coated colors represent achievable colors on a coated material. Uncoated colors represent achievable colors on uncoated material.
Hex Color: Hexadecimal color format. This color mode is intended for viewing on screen and many colors can not be replicated exactly with CMYK printing.
DIGITAL IMAGERY
Bitmap image: image format where shapes and colors are made up of pixels, (examples: JPG, PNG, TIFF, GIF). These images can NOT be scaled up without quality loss, and should be sized for print at a minimum resolution of 300dpi.
Resolution: pixels per inch (ppi), or dots per inch (dpi). 300dpi is the minimum standard resolution for print.
Raster effects: bitmap effects applied to vector images, including drop shadows and outer glows. Document raster effect settings should be set to 300dpi for printing.
Vector image: image format where shapes are made up from mathematical formulas. These images can be scaled up or down without quality loss. Vector images are often created in Adobe Illustrator, or CorelDRAW. (examples: AI, EPS, SVG).
TEMPLATES
Bleed: Printed color or imagery that extends to the edge of the label. The bleed line on a template shows the bleed area, (where the color or image must reach in order to print correctly).
Die line: Line on label template that indicates where the die will cut or perforate the label.
Safety: Line on label template that indicates the maximum safety area on a label, (where type and images can be safely placed to not risk getting cut off the label).
Varnish layer: Area to indicate where varnish areas should print on a label.
White layer: Area to indicate where white areas should print over a metallic stock before the color is printed. You can use gradients and tints of white in the white layer to achieve different effects. The opacity of the color will be guided by the white underneath, with the exception of black, which prints opaque. Please provide the white area on its own layer within the file, using the same safety and bleed areas, and preferably with a swatch applied indicating white in some way.
PHYSICAL
Stock: Term for the material/substrate that is printed on. Label stock consists of three layers: facestock, adhesive, and release liner.
Lamination: clear film applied over the entire label for protection and/or texture.
Spot varnish: finish applied by plate to specific areas of the label for protection and/or texture.
Flood varnish: finish applied by roller over the entire label for protection and/or texture.
Core: Cardboard tube in the center of a roll of labels. The core supports the roll, and is mounted on a spool on label application machine. Cores are typically are sized in 3″ diameter or 1″ diameter.
MAX OD: Maximum outer diameter of a label roll. This measurement is usually specific to each label application machine.
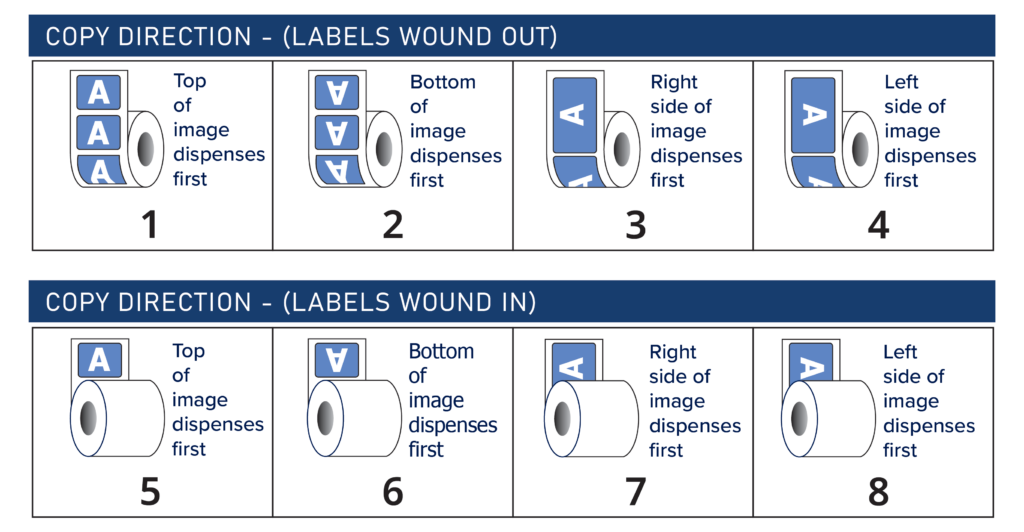
Copy Direction: Numbering system to indicate which portion of the label must head-off the label roll for correct application.
CUTTING
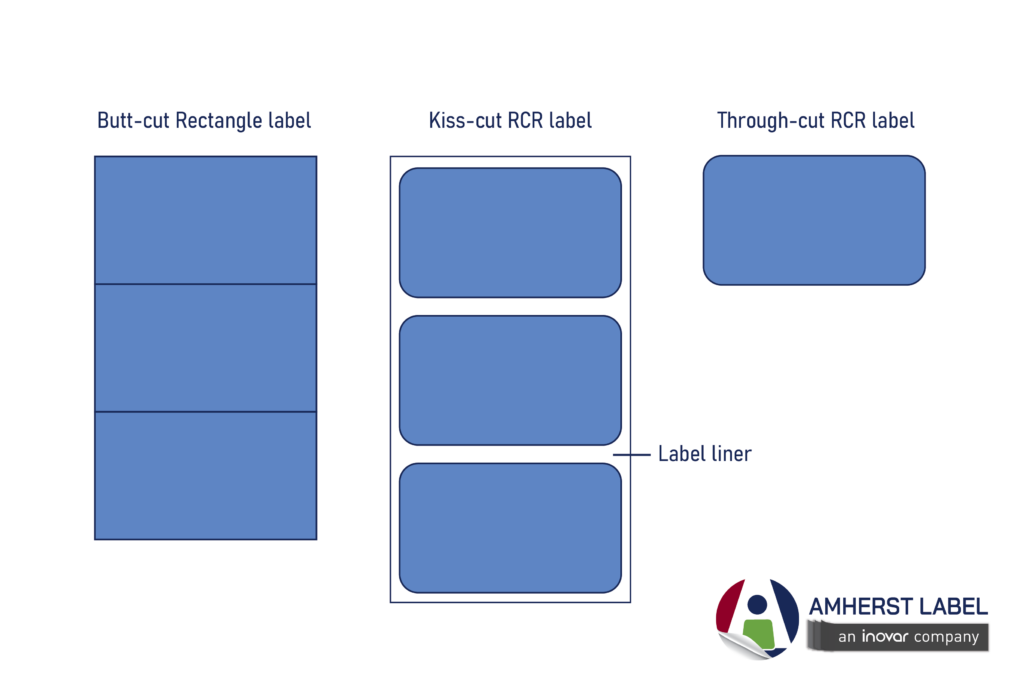
RCR: Round cornered Rectangle
Kiss-cut: When the cutting die cuts through the label but does not cut through the label liner.
Butt-cut: a special cut that cuts across the label roll, leaving no space between labels.
Waste matrix: remaining label material that surrounds the kiss-cut label on the roll or sheet. On rolls, the waste matrix is stripped away. On sheets, the waste matrix is often left on the sheet.
Perf: Perforation created with a cutting tool. The sequence of small cuts enable the material to fold or tear more easily in a desired location.